|
HARM
harm and utilities
|
Sets metric in some coordinates based upon metric.h type choice for MCOORD this file includes metric dependent terms, including for initial condition routines for IC coords. More...
#include "decs.h"
Go to the source code of this file.
Macros | |
| #define | FLATSPACE 0 |
| #define | NOSPIN 1 |
| #define | FULLHT 2 |
| #define | HTMETRICTYPE FULLHT |
| #define | FLATSPACE 0 |
| #define | NOSPIN 1 |
| #define | FULLHT 2 |
| #define | HTMETRICTYPE FULLHT |
| #define | ks_gcov00 (-1. + MSQ/rho2small) |
| #define | ks_gcov01 (MSQ/rho2small) |
| #define | ks_gcov02 (0) |
| #define | ks_gcov03 (-MSQ*a*s2/rho2small) |
| #define | ks_gcov10 (ks_gcov01) |
| #define | ks_gcov11 (1. + MSQ/rho2small) |
| #define | ks_gcov12 (0) |
| #define | ks_gcov13 (-a*s2*(1. + MSQ/rho2small)) |
| #define | ks_gcov20 (0) |
| #define | ks_gcov21 (0) |
| #define | ks_gcov22 (rho2) |
| #define | ks_gcov23 (0) |
| #define | ks_gcov30 (ks_gcov03) |
| #define | ks_gcov31 (ks_gcov13) |
| #define | ks_gcov32 (0) |
| #define | ks_gcov33 (s2*(rho2 + a*a*s2*(1. + MSQ/rho2small))) |
| #define | bl_gcov00 (-(1. - MSQ/(r2small*mu))) |
| #define | bl_gcov01 (0) |
| #define | bl_gcov02 (0) |
| #define | bl_gcov03 (-MSQ*a*s2/(r2small*mu)) |
| #define | bl_gcov10 (0) |
| #define | bl_gcov11 (mu/DD) |
| #define | bl_gcov12 (0) |
| #define | bl_gcov13 (0) |
| #define | bl_gcov20 (0) |
| #define | bl_gcov21 (0) |
| #define | bl_gcov22 (r2*mu) |
| #define | bl_gcov23 (0) |
| #define | bl_gcov30 (bl_gcov03) |
| #define | bl_gcov31 (0) |
| #define | bl_gcov32 (0) |
| #define | bl_gcov33 (r2*sth*sth*(1. + a2/r2small + MSQ*a2*s2/(r2small*r2small*mu))) |
| #define | ks_gcon00 (-(1.+ MSQ/rho2)) |
| #define | ks_gcon01 (MSQ/rho2) |
| #define | ks_gcon02 (0) |
| #define | ks_gcon03 (0) |
| #define | ks_gcon10 (ks_gcon01) |
| #define | ks_gcon11 ((r*r+a*a-MSQ)/rho2) |
| #define | ks_gcon12 (0) |
| #define | ks_gcon13 (a/rho2) |
| #define | ks_gcon20 (ks_gcon02) |
| #define | ks_gcon21 (ks_gcon12) |
| #define | ks_gcon22 (1./rho2) |
| #define | ks_gcon23 (0) |
| #define | ks_gcon30 (ks_gcon03) |
| #define | ks_gcon31 (ks_gcon13) |
| #define | ks_gcon32 (ks_gcon23) |
| #define | ks_gcon33 (1./(rho2*s2)) |
| #define | bl_gcon00 (-1. - MSQ*(1. + a2/r2small)/(r2small*DD*mu)) |
| #define | bl_gcon01 (0) |
| #define | bl_gcon02 (0) |
| #define | bl_gcon03 (-MSQ*a/(r2small*r2small*DD*mu)) |
| #define | bl_gcon10 (0) |
| #define | bl_gcon11 (DD/mu) |
| #define | bl_gcon12 (0) |
| #define | bl_gcon13 (0) |
| #define | bl_gcon20 (0) |
| #define | bl_gcon21 (0) |
| #define | bl_gcon22 (1./(r2small*mu)) |
| #define | bl_gcon23 (0) |
| #define | bl_gcon30 (bl_gcon03) |
| #define | bl_gcon31 (0) |
| #define | bl_gcon32 (0) |
| #define | bl_gcon33 ((1. - MSQ/(r2small*mu))/(r2small*sth*sth*DD)) |
| #define | M (1.) |
| #define | IDXR(a, R0, r, th, rl, rh) ((pow(a,2) + 2.*pow(r,2) + pow(a,2)*cos(2.*th))/((rh - 1.*rl)*(2.*R0 + rh + rl) + (pow(a,2) + 2.*pow(R0,2))*(log(-1.*R0 + rh) - 1.*log(-1.*R0 + rl)) + pow(a,2)*cos(2.*th)*(log(-1.*R0 + rh) - 1.*log(-1.*R0 + rl)))) |
| #define | IDXTH(a, R0, r, th, thl, thh) ((-3.*M_PI*(pow(a,2) + 2.*pow(r,2) + pow(a,2)*cos(2.*th))*sin(th))/(cos(thh)*(pow(a,2) + 6.*pow(r,2) + pow(a,2)*cos(2.*thh)) - 1.*cos(thl)*(pow(a,2) + 6.*pow(r,2) + pow(a,2)*cos(2.*thl)))) |
| #define | FIDXR(a, R0, r, th) ((pow(a,2) + 2.*pow(r,2) + pow(a,2)*cos(2.*th))/(4.*R0*(-1.*R0 + r) + pow(-1.*R0 + r,2) + (pow(a,2) + 2.*pow(R0,2) + pow(a,2)*cos(2.*th))*log(-1.*R0 + r))) |
| #define | FIDXTH(a, R0, r, th) ((-3.*pow(a,2)*sin(2.*th) - 6.*pow(r,2)*tan(th))/(pow(a,2) + 6.*pow(r,2) + pow(a,2)*cos(2.*th))) |
Functions | |
| void | gcov_func (struct of_geom *ptrgeom, int getprim, int whichcoord, FTYPE *X, FTYPE *gcovinfunc, FTYPE *gcovpertinfunc) |
| obtain gcov in primcoords of whichcoord type metric/coords here ptrgeom is only expected to contain i,j,k,p location More... | |
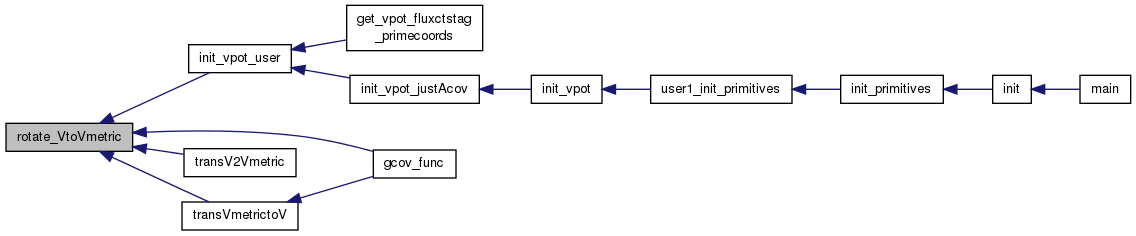
| int | rotate_VtoVmetric (int whichcoord, FTYPE ROTANGLE, FTYPE *V, FTYPE *Vmetric) |
| Rotate V[X] (r,thnew,phnew as in bl_coord) to Vmetric (r,th,ph as in set_gcov) That is, when using rotated metric, we assume metric itself still has Vmetric=r,th,ph, while X is mapped to V=rnew,hnew,phnew. More... | |
| int | rotate_VmetrictoV (int whichcoord, FTYPE ROTANGLE, FTYPE *Vmetric, FTYPE *V) |
| perform rotation of V (for spherical polar coordinates) More... | |
| void | gcon_func (struct of_geom *ptrgeom, int getprim, int whichcoord, FTYPE *X, FTYPE *gcov, FTYPE *gcon) |
| obtain prim gcon in primcoords of whichcoord type metric/coords More... | |
| void | conn_func (int whichcoord, FTYPE *X, struct of_geom *geom, FTYPE(*conn)[NDIM][NDIM], FTYPE *conn2) |
| connection not simply transformed – so compute directly from final metric (primcoords) More... | |
| void | set_gcov_ksmetric (FTYPE *V, FTYPE *gcov, FTYPE *gcovpert) |
| (~t,r,,~) More... | |
| void | set_gcon_ksmetric (FTYPE *V, FTYPE *gcon) |
| g^{} (analytic or numerical) More... | |
| void | set_conn_general (FTYPE *X, struct of_geom *geom, FTYPE(*conn)[NDIM][NDIM], FTYPE *conn2) |
| CONNECTIONS (numerical or analytic) More... | |
| void | set_conn_ksmetric (FTYPE *X, struct of_geom *geom, FTYPE(*conn)[NDIM][NDIM], FTYPE *conn2) |
| void | gdetvol_func (struct of_geom *ptrgeom, FTYPE *gdettrue, FTYPE *EOMFUNCNAME, FTYPE *gdetvol) |
| geometry only contains i,j,k,p only for spherical polar coordinates with negligible relativistic effects only used if GDETVOLDIFF==1 More... | |
Sets metric in some coordinates based upon metric.h type choice for MCOORD this file includes metric dependent terms, including for initial condition routines for IC coords.
crucially need to setup analytic form of gcov. All rest can be done numerically or analytically if wanted. SUPERNOTE: Set DOMIXTHETAPHI to 0 or 1 in definit.h!! self-gravity TODO: http://www.fftw.org/ COSMOS++ uses: https://computation.llnl.gov/casc/hypre/software.html http://ciera.northwestern.edu/StarCrash/manual/html/node3.html http://ccfd-jacob.blogspot.com http://farside.ph.utexas.edu/teaching/329/lectures/node60.html
Definition in file metric.c.
| #define bl_gcon00 (-1. - MSQ*(1. + a2/r2small)/(r2small*DD*mu)) |
| #define bl_gcon01 (0) |
| #define bl_gcon02 (0) |
| #define bl_gcon10 (0) |
| #define bl_gcon11 (DD/mu) |
| #define bl_gcon12 (0) |
| #define bl_gcon13 (0) |
| #define bl_gcon20 (0) |
| #define bl_gcon21 (0) |
| #define bl_gcon22 (1./(r2small*mu)) |
| #define bl_gcon23 (0) |
| #define bl_gcon30 (bl_gcon03) |
| #define bl_gcon31 (0) |
| #define bl_gcon32 (0) |
| #define bl_gcon33 ((1. - MSQ/(r2small*mu))/(r2small*sth*sth*DD)) |
| #define bl_gcov00 (-(1. - MSQ/(r2small*mu))) |
| #define bl_gcov01 (0) |
| #define bl_gcov02 (0) |
| #define bl_gcov10 (0) |
| #define bl_gcov11 (mu/DD) |
| #define bl_gcov12 (0) |
| #define bl_gcov13 (0) |
| #define bl_gcov20 (0) |
| #define bl_gcov21 (0) |
| #define bl_gcov22 (r2*mu) |
| #define bl_gcov23 (0) |
| #define bl_gcov30 (bl_gcov03) |
| #define bl_gcov31 (0) |
| #define bl_gcov32 (0) |
| #define bl_gcov33 (r2*sth*sth*(1. + a2/r2small + MSQ*a2*s2/(r2small*r2small*mu))) |
| #define FIDXR | ( | a, | |
| R0, | |||
| r, | |||
| th | |||
| ) | ((pow(a,2) + 2.*pow(r,2) + pow(a,2)*cos(2.*th))/(4.*R0*(-1.*R0 + r) + pow(-1.*R0 + r,2) + (pow(a,2) + 2.*pow(R0,2) + pow(a,2)*cos(2.*th))*log(-1.*R0 + r))) |
| #define FIDXTH | ( | a, | |
| R0, | |||
| r, | |||
| th | |||
| ) | ((-3.*pow(a,2)*sin(2.*th) - 6.*pow(r,2)*tan(th))/(pow(a,2) + 6.*pow(r,2) + pow(a,2)*cos(2.*th))) |
| #define FLATSPACE 0 |
| #define FLATSPACE 0 |
| #define FULLHT 2 |
| #define FULLHT 2 |
| #define HTMETRICTYPE FULLHT |
| #define HTMETRICTYPE FULLHT |
| #define IDXR | ( | a, | |
| R0, | |||
| r, | |||
| th, | |||
| rl, | |||
| rh | |||
| ) | ((pow(a,2) + 2.*pow(r,2) + pow(a,2)*cos(2.*th))/((rh - 1.*rl)*(2.*R0 + rh + rl) + (pow(a,2) + 2.*pow(R0,2))*(log(-1.*R0 + rh) - 1.*log(-1.*R0 + rl)) + pow(a,2)*cos(2.*th)*(log(-1.*R0 + rh) - 1.*log(-1.*R0 + rl)))) |
| #define IDXTH | ( | a, | |
| R0, | |||
| r, | |||
| th, | |||
| thl, | |||
| thh | |||
| ) | ((-3.*M_PI*(pow(a,2) + 2.*pow(r,2) + pow(a,2)*cos(2.*th))*sin(th))/(cos(thh)*(pow(a,2) + 6.*pow(r,2) + pow(a,2)*cos(2.*thh)) - 1.*cos(thl)*(pow(a,2) + 6.*pow(r,2) + pow(a,2)*cos(2.*thl)))) |
| #define ks_gcon00 (-(1.+ MSQ/rho2)) |
| #define ks_gcon01 (MSQ/rho2) |
| #define ks_gcon02 (0) |
| #define ks_gcon03 (0) |
| #define ks_gcon10 (ks_gcon01) |
| #define ks_gcon12 (0) |
| #define ks_gcon13 (a/rho2) |
| #define ks_gcon20 (ks_gcon02) |
| #define ks_gcon21 (ks_gcon12) |
| #define ks_gcon22 (1./rho2) |
| #define ks_gcon23 (0) |
| #define ks_gcon30 (ks_gcon03) |
| #define ks_gcon31 (ks_gcon13) |
| #define ks_gcon32 (ks_gcon23) |
| #define ks_gcon33 (1./(rho2*s2)) |
| #define ks_gcov00 (-1. + MSQ/rho2small) |
| #define ks_gcov01 (MSQ/rho2small) |
| #define ks_gcov02 (0) |
| #define ks_gcov03 (-MSQ*a*s2/rho2small) |
| #define ks_gcov10 (ks_gcov01) |
| #define ks_gcov11 (1. + MSQ/rho2small) |
| #define ks_gcov12 (0) |
| #define ks_gcov13 (-a*s2*(1. + MSQ/rho2small)) |
| #define ks_gcov20 (0) |
| #define ks_gcov21 (0) |
| #define ks_gcov22 (rho2) |
| #define ks_gcov23 (0) |
| #define ks_gcov30 (ks_gcov03) |
| #define ks_gcov31 (ks_gcov13) |
| #define ks_gcov32 (0) |
| #define NOSPIN 1 |
| #define NOSPIN 1 |
perform rotation of V (for spherical polar coordinates)
This takes input of V=(t,r,h,ph) and gives back Vmetric=(t,r,hnew,phnew) where h,ph are in original metric form and hnew,phnew are rotated versions
So since we want X->V to be mapping V=(t,r,hnew,phnew), this is not to be used.
This can be used in (e.g.) init.py to have python script take data (in Vnew=V) and obtain Vmetric version
1) transVtoVmetric(gcovnew) gives gcov[original metric] 2) transVtoVmetric(ucon,bcon,ucov,bcov) or transVmetrictoV(ucon,bcon,ucov,bcov) 3) Rotate actual spatial positions of data, including metrics, so that again axisymmetric so only have to store 1 phi slice!
Rotate V[X] (r,thnew,phnew as in bl_coord) to Vmetric (r,th,ph as in set_gcov) That is, when using rotated metric, we assume metric itself still has Vmetric=r,th,ph, while X is mapped to V=rnew,hnew,phnew.
So input to set_gcov(X,V) needs to then get V->Vmetric before getting gcov(Vmetric). So real spherical polar coordinates for grid itself is V=rnew,hnew,phnew.
Use this rather than direct transformation(rnew,hnew,phnew) because that expression becomes too complicated in mathematica. So just take 3 steps: 1) gcov_func(X,V) 2) rotate_VtoVmetric(V,Vmetric) 3) set_gcov...(Vmetric) 4) transVmetrictoV(gcov) (which internally uses rotate_VtoVmetric() to keep expressions simple (i.e. kept in terms of Vmetric)
#2 just accounts for Vmetric[V[X]] as far as assignment of metric values so that X[] grid has used correct values of old/metric r,h,ph #4 accounts for differentials in metric so that ds^2 is the same. This is written in terms of V=rnew,hnew,phnew, so can just feed-in V[X].
Definition at line 378 of file metric.c.
 1.8.3.1
1.8.3.1